FIVE things to consider before purchasing a temperature and humidity test chamber 2/3
3.Temperature change rateFor temperature testing, there are different types of profiles. These tests can be divided into three categories:
3.1 constant temperature or temperature cycle test
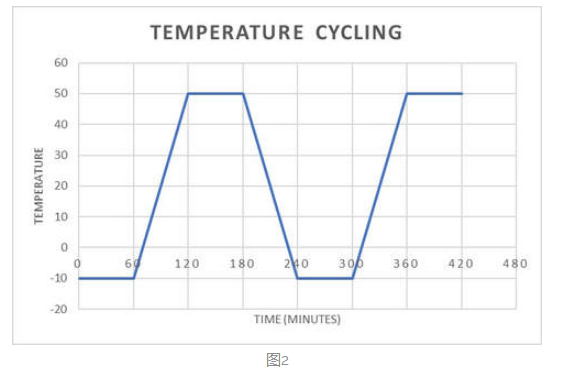 Figure 2
Figure 2For thermostatic testing, set it to the duration specified at the specified temperature. while for temperature cycle test, temperature can be multiple temperatures with different duration.
Figure 2 illustrates the typical temperature cycle test curve. Most importantly, the temperature change rate of heating is usually not greater than 3°C /min, and the temperature change rate of cooling is usually not higher than 1°C /min.
3.2 Rapid Temperature Change Test
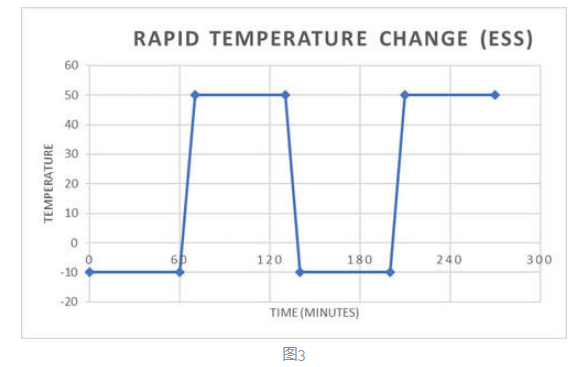 Figure 3
Figure 3
Similar to the above temperature test cycles, rapid temperature tests perform temperature changes at a higher rate (i.e., up to 20°C per minute), respectively. this test is also commonly referred to as ESS( ambient pressure screening), HALT( highly accelerated pressure testing) or HASS( highly accelerated pressure screening). The purpose of this test is to enable you to evaluate product quality against rapid changes in temperature.
Figure 3 shows the rapid temperature change cycle test. It is important to note that the temperature of the part (specimen) is always lower than the air temperature in the chamber.
3.3 Thermal shock
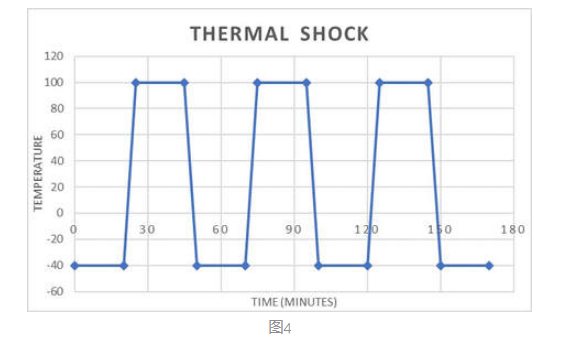
In thermal shock testing, the product is repeatedly subjected to extremely low and high temperature changes at a very fast transition speed. The test will stimulate the product acceleration stress caused by thermal shock during normal use.
Changes in temperature between low and high temperatures are very rapid, more than 15°C per minute
The chamber manufacturer will have the airflow inside the chamber designed so that the airflow has sufficient volume to move the air temperature at a partial temperature at a rate.
Heat shock test boxes are usually divided into 3 or 2 zones
For the thermal shock chamber in three zones, the chamber consists of high temperature area, low temperature area and test area. Place the product in the test area and blow alternately into cold and hot air from each chamber.
Some equipment uses two separate hot and cold chambers (2 zones) and a lifting mechanism for the products passing through these 2 compartments.
.jpg)


























